Table of Contents
ToggleIn a world where everything seems to be made of plastic and dreams, titanium 3D printing emerges as the superhero we didn’t know we needed. Imagine crafting complex structures that can withstand the test of time, all while being lighter than a feather and stronger than your morning coffee. It’s not just a trend; it’s a revolution in manufacturing that’s reshaping industries from aerospace to medical devices.
But why settle for ordinary when you can print with titanium? This remarkable metal boasts an impressive strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional corrosion resistance. Whether it’s for a custom prosthetic or a high-performance jet engine part, titanium 3D printing offers endless possibilities. So buckle up and get ready to explore how this cutting-edge technology is transforming the way we create and innovate.
Overview Of Titanium 3D Printing
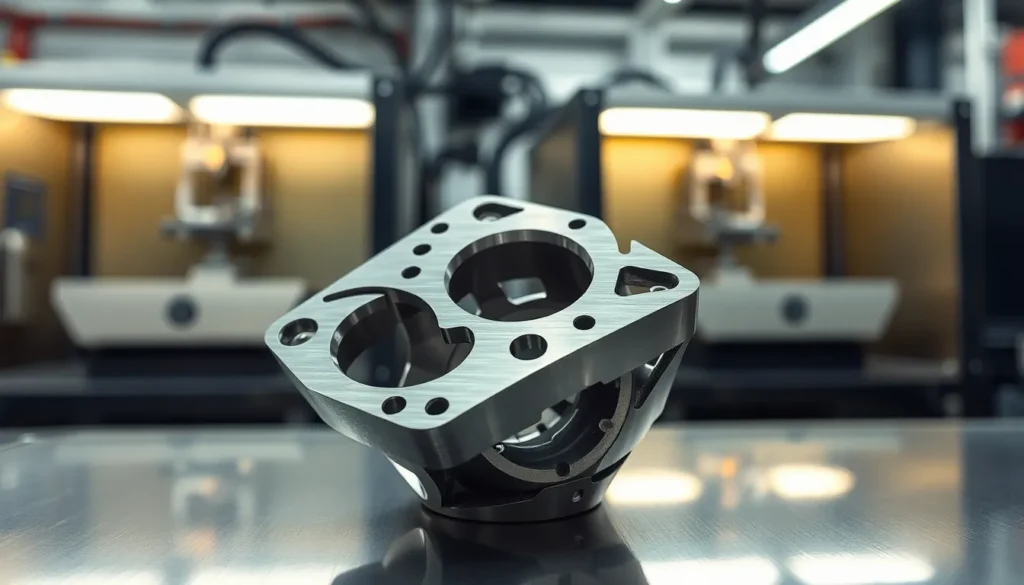
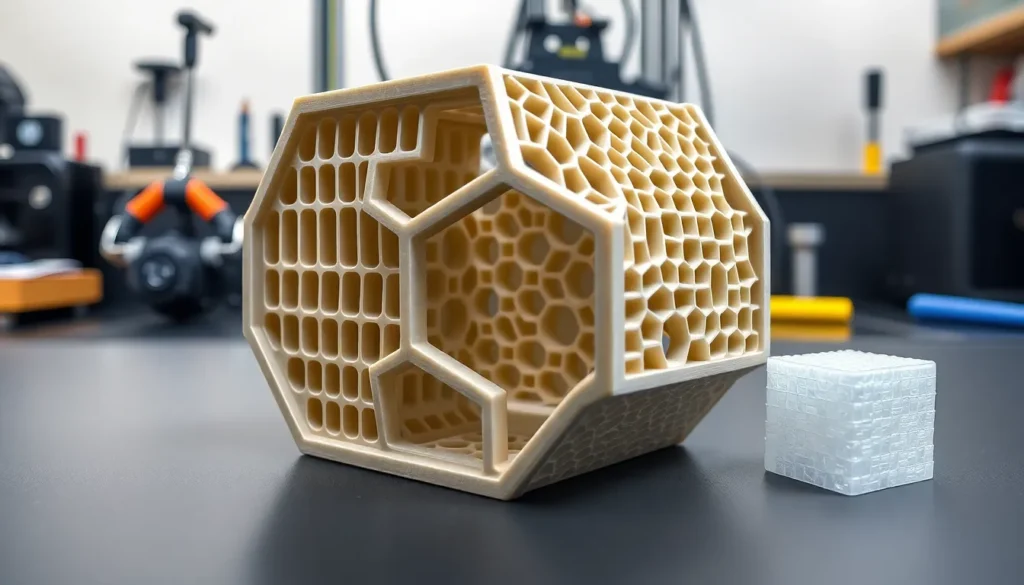
Titanium 3D printing utilizes advanced additive manufacturing techniques to produce parts with remarkable strength and lightweight characteristics. This technology employs various methods, including Selective Laser Melting (SLM) and Electron Beam Melting (EBM), to fuse titanium powder layer by layer. Industries like aerospace, medical, and automotive increasingly rely on titanium for its remarkable properties.
Applications in aerospace include producing components that must endure extreme conditions. Engine parts, structural elements, and brackets highlight titanium’s strength-to-weight ratio, enhancing overall aircraft performance. Medical implants also leverage titanium 3D printing, providing customized solutions for patients. The biocompatibility of titanium ensures safety for long-term implantation.
Cost-effective manufacturing emerges as a significant advantage of this process. Reducing waste materials leads to decreased production costs compared to traditional methods. Complex geometries that were previously impossible become achievable, allowing for innovative designs that enhance functionality. Production speeds also improve, making rapid prototyping and small batch manufacturing more practical.
Post-processing typically occurs after printing. Surface finishing, heat treatments, and machining improve the final product’s properties. These steps customize components to meet specific performance requirements.
Sustainability gains traction with titanium 3D printing. Recyclable titanium powders minimize environmental impact, supporting eco-friendly manufacturing practices. Increased efficiency in material usage contributes to sustainable development in manufacturing sectors, aligning with modern industry trends.
Overall, titanium 3D printing represents a significant leap forward in manufacturing technology, driving advancements across multiple fields and setting new standards for performance and innovation.
Benefits Of Titanium 3D Printing

Titanium 3D printing offers remarkable advantages that enhance manufacturing processes across various industries.
Lightweight Properties
Titanium’s lightweight nature plays a crucial role in industries like aerospace and automotive. Reduced weight translates to improved fuel efficiency and performance. This property allows for the creation of components that don’t compromise strength while minimizing overall mass. Aerospace manufacturers benefit significantly as lighter parts reduce the load on engines, enhancing operational efficiency. Innovations in design enabled by titanium’s lightweight characteristics make complex geometries possible, pushing the boundaries of traditional manufacturing methods.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
A key advantage of titanium is its high strength-to-weight ratio. This property allows parts to withstand extreme stress without adding significant weight. Aerospace engineers rely on this feature for critical components that require durability under demanding conditions. High-performance applications often call for materials that resist deformation and fatigue, and titanium meets these needs effectively. This unique combination supports the production of parts that ensure safety and reliability, particularly in fields such as defense and medical devices.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion resistance further enhances titanium’s appeal. The material can resist the damaging effects of harsh environments, making it ideal for chemical processing and marine applications. Even in extreme conditions, titanium maintains its integrity, ensuring longevity. Medical implants also benefit from this quality, as titanium can withstand bodily fluids without degrading. The corrosion-resistant nature contributes to lower maintenance costs and improved service life, ensuring components perform optimally throughout their lifespan.
Applications Of Titanium 3D Printing
Titanium 3D printing transforms several industries. Its unique attributes, including strength and lightweight features, open new possibilities.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace relies heavily on titanium 3D printing for creating components. Structures such as engine parts, brackets, and housing benefit from titanium’s high strength-to-weight ratio. Complex geometries achievable by additive manufacturing enhance performance and reduce weight significantly. Components produced with Selective Laser Melting exhibit durability under extreme conditions. Moreover, using titanium decreases fuel consumption, improving overall aircraft efficiency. Maintenance intervals lengthen due to titanium’s resistance to corrosion, directly influencing operational costs.
Medical Implants
In the medical field, titanium 3D printing revolutionizes implant manufacturing. Custom implants tailored to a patient’s unique anatomy ensure a better fit and increased comfort. Biocompatibility of titanium reduces the risk of rejection, enhancing patient outcomes. Applications range from dental implants to orthopedic devices, showcasing versatility. Personalized surgical guides and prosthetics created through this technology streamline surgical procedures. Enhanced integration with bone tissue also contributes to faster recovery times, addressing patient needs effectively.
Automotive Developments
Automotive innovation benefits greatly from titanium 3D printing. Lightweight components allow for improved fuel efficiency and performance. Parts designed for high-stress applications, such as suspension systems and exhaust components, see significant enhancements in strength. Rapid prototyping capabilities support manufacturers in testing new designs quickly. Additionally, reduced material waste during production contributes to cost savings and sustainability efforts. The integration of titanium parts aids in meeting industry standards for safety and performance, driving advancements forward.
Challenges In Titanium 3D Printing
Titanium 3D printing presents several challenges that can impact its widespread adoption and efficiency.
Cost Analysis
Cost considerations significantly influence the titanium 3D printing process. Material costs for titanium powders remain high, making initial investments substantial for manufacturers. The expense associated with advanced machines also leads to increased production costs. Additionally, post-processing can further elevate expenses, requiring specialized equipment and skilled personnel. Reduced waste and improved production speeds help offset some costs, but financial barriers often deter smaller companies from entering the market. Organizations must meticulously analyze their budgets to assess the feasibility of adopting this technology.
Technical Limitations
Technical hurdles impact the effectiveness of titanium 3D printing. Certain methods, such as Selective Laser Melting, face challenges in achieving optimal layer adhesion, which can affect structural integrity. Defects like porosity may arise during the printing process, undermining the properties of the final product. Furthermore, achieving consistent quality across different batches remains a significant challenge. Complicated geometries may also complicate the printing process, leading to longer lead times. Addressing these limitations requires ongoing research and development to enhance material properties and refine machine capabilities.
Future Trends In Titanium 3D Printing
Advancements in titanium 3D printing technology promise to reshape manufacturing. Enhanced materials development leads to stronger, more durable titanium alloys. Researchers increasingly focus on refining powder quality to reduce defects and improve print consistency.
Integration of artificial intelligence improves the efficiency of printing processes. AI optimizes parameters, reducing waste and enhancing speed while maintaining quality. This trend positions titanium 3D printing for greater scalability across various industries.
Emerging applications in the automotive sector highlight its impact on vehicle design. Engineers explore opportunities for creating lightweight components that enhance fuel efficiency. Innovations in custom parts cater not only to performance but also to aesthetic preferences.
Sustainability initiatives gain traction within the titanium 3D printing landscape. Manufacturers invest in recycling technologies to reclaim titanium powder, minimizing waste and resource consumption. Eco-friendly practices align with global sustainability goals, attracting more companies to this technology.
Collaboration between universities and industry players fosters innovation. Joint projects aim to tackle existing technical challenges, such as layer adhesion and porosity. This collaboration drives forward-thinking solutions that enhance overall product integrity.
Market demand for personalized medical devices expands opportunities. Titanium 3D printing enables the production of tailored implants significant to patient outcomes. Surgeons appreciate the ability to create anatomically correct structures that streamline procedures.
Evolving regulatory frameworks support the growth of titanium 3D printing. Authorities recognize the importance of additive manufacturing in sectors like aerospace and healthcare. Compliance with new standards ensures safety and reliability, building confidence among manufacturers.
Continuous research explores novel printing techniques, such as hybrid systems combining traditional methods with additive processes. These developments may lead to further efficiency gains and cost reductions. The future of titanium 3D printing holds immense potential, promising to revolutionize complex manufacturing processes across multiple fields.
Titanium 3D printing stands at the forefront of manufacturing innovation. Its unique properties and versatility continue to reshape industries like aerospace and healthcare. As companies strive for efficiency and sustainability, titanium’s lightweight and durable characteristics offer significant advantages.
The ongoing research and development efforts promise to address existing challenges, paving the way for broader adoption. With advancements in materials and processing technologies, the future looks bright for titanium 3D printing. This technology not only enhances production capabilities but also aligns with global sustainability goals, making it a key player in the evolution of modern manufacturing. As it evolves, titanium 3D printing will undoubtedly continue to drive remarkable advancements across various sectors.